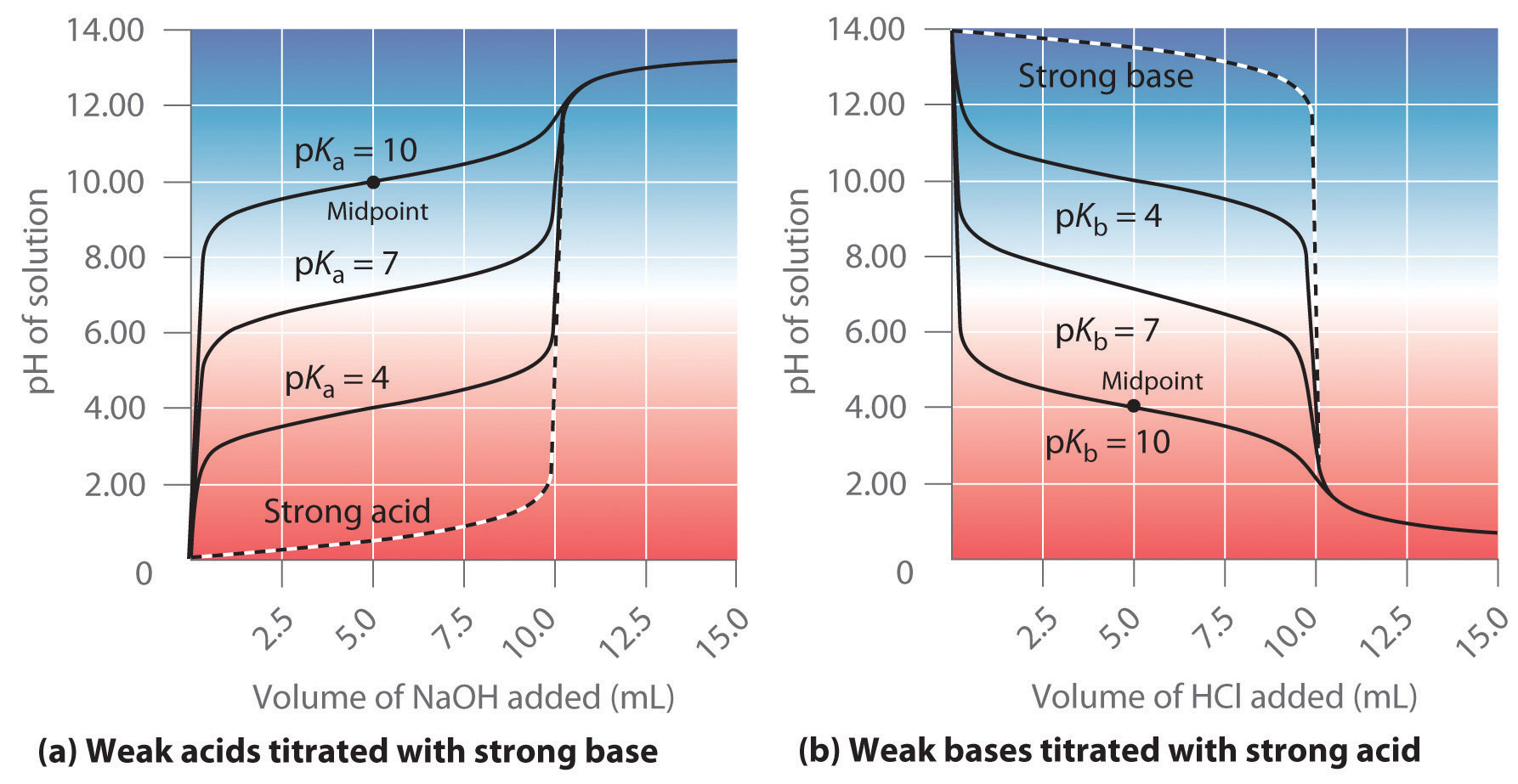
Titration Base Concentration . \(\text{m}_a\) is the molarity of the acid, while \(\text{m}_b\) is the molarity of the base. A titration is carried out for 25.00 ml of 0.100 m hcl (strong acid) with 0.100 m of a strong base naoh (the titration curve is shown in figure. A titration is a laboratory technique used to precisely measure molar concentration of an unknown solution using a known solution. The analyte (titrand) is the solution with an unknown molarity. In a titration, a solution of known concentration (the titrant) is added to a solution of the substance being studied (the analyte). Titration is performed by slowly adding a solution of known concentration to a solution of unknown concentration while observing the reaction. \(\text{v}_a\) and \(\text{v}_b\) are the.
from webmis.highland.cc.il.us
In a titration, a solution of known concentration (the titrant) is added to a solution of the substance being studied (the analyte). Titration is performed by slowly adding a solution of known concentration to a solution of unknown concentration while observing the reaction. The analyte (titrand) is the solution with an unknown molarity. \(\text{m}_a\) is the molarity of the acid, while \(\text{m}_b\) is the molarity of the base. A titration is a laboratory technique used to precisely measure molar concentration of an unknown solution using a known solution. A titration is carried out for 25.00 ml of 0.100 m hcl (strong acid) with 0.100 m of a strong base naoh (the titration curve is shown in figure. \(\text{v}_a\) and \(\text{v}_b\) are the.
AcidBase Titrations
Titration Base Concentration The analyte (titrand) is the solution with an unknown molarity. The analyte (titrand) is the solution with an unknown molarity. A titration is a laboratory technique used to precisely measure molar concentration of an unknown solution using a known solution. In a titration, a solution of known concentration (the titrant) is added to a solution of the substance being studied (the analyte). \(\text{v}_a\) and \(\text{v}_b\) are the. A titration is carried out for 25.00 ml of 0.100 m hcl (strong acid) with 0.100 m of a strong base naoh (the titration curve is shown in figure. Titration is performed by slowly adding a solution of known concentration to a solution of unknown concentration while observing the reaction. \(\text{m}_a\) is the molarity of the acid, while \(\text{m}_b\) is the molarity of the base.
From www.scienceabc.com
Titration Chemistry Definition, Explanation, Formula And Calculation Titration Base Concentration Titration is performed by slowly adding a solution of known concentration to a solution of unknown concentration while observing the reaction. The analyte (titrand) is the solution with an unknown molarity. A titration is a laboratory technique used to precisely measure molar concentration of an unknown solution using a known solution. In a titration, a solution of known concentration (the. Titration Base Concentration.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Unit 19 Acid Base Equilibria Titrations PowerPoint Presentation Titration Base Concentration \(\text{v}_a\) and \(\text{v}_b\) are the. \(\text{m}_a\) is the molarity of the acid, while \(\text{m}_b\) is the molarity of the base. Titration is performed by slowly adding a solution of known concentration to a solution of unknown concentration while observing the reaction. A titration is carried out for 25.00 ml of 0.100 m hcl (strong acid) with 0.100 m of a. Titration Base Concentration.
From psu.pb.unizin.org
14.7 AcidBase Titrations Chemistry 112 Chapters 1217 of OpenStax Titration Base Concentration A titration is carried out for 25.00 ml of 0.100 m hcl (strong acid) with 0.100 m of a strong base naoh (the titration curve is shown in figure. Titration is performed by slowly adding a solution of known concentration to a solution of unknown concentration while observing the reaction. A titration is a laboratory technique used to precisely measure. Titration Base Concentration.
From www.studocu.com
Acid Base Titration Worksheetcalculations including molar Titration Base Concentration A titration is carried out for 25.00 ml of 0.100 m hcl (strong acid) with 0.100 m of a strong base naoh (the titration curve is shown in figure. Titration is performed by slowly adding a solution of known concentration to a solution of unknown concentration while observing the reaction. In a titration, a solution of known concentration (the titrant). Titration Base Concentration.
From letitsnowglobe.co.uk
Titration procedure pdf Titration Base Concentration \(\text{v}_a\) and \(\text{v}_b\) are the. A titration is a laboratory technique used to precisely measure molar concentration of an unknown solution using a known solution. A titration is carried out for 25.00 ml of 0.100 m hcl (strong acid) with 0.100 m of a strong base naoh (the titration curve is shown in figure. \(\text{m}_a\) is the molarity of the. Titration Base Concentration.
From www.youtube.com
Determining the concentration by acid base titration YouTube Titration Base Concentration \(\text{m}_a\) is the molarity of the acid, while \(\text{m}_b\) is the molarity of the base. \(\text{v}_a\) and \(\text{v}_b\) are the. A titration is carried out for 25.00 ml of 0.100 m hcl (strong acid) with 0.100 m of a strong base naoh (the titration curve is shown in figure. The analyte (titrand) is the solution with an unknown molarity. Titration. Titration Base Concentration.
From www.youtube.com
Conductometric Titration & Titration Curves // HSC Chemistry YouTube Titration Base Concentration \(\text{v}_a\) and \(\text{v}_b\) are the. A titration is carried out for 25.00 ml of 0.100 m hcl (strong acid) with 0.100 m of a strong base naoh (the titration curve is shown in figure. \(\text{m}_a\) is the molarity of the acid, while \(\text{m}_b\) is the molarity of the base. The analyte (titrand) is the solution with an unknown molarity. A. Titration Base Concentration.
From www.vecteezy.com
Acid Base titration involves Precisely measures solution concentration Titration Base Concentration \(\text{m}_a\) is the molarity of the acid, while \(\text{m}_b\) is the molarity of the base. Titration is performed by slowly adding a solution of known concentration to a solution of unknown concentration while observing the reaction. A titration is a laboratory technique used to precisely measure molar concentration of an unknown solution using a known solution. A titration is carried. Titration Base Concentration.
From www.priyamstudycentre.com
Acid Base Titration Principle, Types, Process, Indicators Titration Base Concentration A titration is a laboratory technique used to precisely measure molar concentration of an unknown solution using a known solution. \(\text{v}_a\) and \(\text{v}_b\) are the. In a titration, a solution of known concentration (the titrant) is added to a solution of the substance being studied (the analyte). \(\text{m}_a\) is the molarity of the acid, while \(\text{m}_b\) is the molarity of. Titration Base Concentration.
From www.flinnsci.com
AcidBase Titrations—Classic Lab Kit for AP® Chemistry Flinn Scientific Titration Base Concentration The analyte (titrand) is the solution with an unknown molarity. \(\text{m}_a\) is the molarity of the acid, while \(\text{m}_b\) is the molarity of the base. Titration is performed by slowly adding a solution of known concentration to a solution of unknown concentration while observing the reaction. \(\text{v}_a\) and \(\text{v}_b\) are the. A titration is a laboratory technique used to precisely. Titration Base Concentration.
From chemistrymadesimple.net
What is Titration and How is it Done? Chemistry Made Simple Titration Base Concentration A titration is a laboratory technique used to precisely measure molar concentration of an unknown solution using a known solution. \(\text{v}_a\) and \(\text{v}_b\) are the. A titration is carried out for 25.00 ml of 0.100 m hcl (strong acid) with 0.100 m of a strong base naoh (the titration curve is shown in figure. The analyte (titrand) is the solution. Titration Base Concentration.
From chem.libretexts.org
17.3 AcidBase Titrations Chemistry LibreTexts Titration Base Concentration A titration is carried out for 25.00 ml of 0.100 m hcl (strong acid) with 0.100 m of a strong base naoh (the titration curve is shown in figure. \(\text{v}_a\) and \(\text{v}_b\) are the. A titration is a laboratory technique used to precisely measure molar concentration of an unknown solution using a known solution. \(\text{m}_a\) is the molarity of the. Titration Base Concentration.
From www.vecteezy.com
Acid base titration experiment and phases of color change during Titration Base Concentration \(\text{m}_a\) is the molarity of the acid, while \(\text{m}_b\) is the molarity of the base. A titration is carried out for 25.00 ml of 0.100 m hcl (strong acid) with 0.100 m of a strong base naoh (the titration curve is shown in figure. Titration is performed by slowly adding a solution of known concentration to a solution of unknown. Titration Base Concentration.
From present5.com
AcidBase Titrations Barb Fallon AP Chemistry June 2007 Titration Base Concentration The analyte (titrand) is the solution with an unknown molarity. In a titration, a solution of known concentration (the titrant) is added to a solution of the substance being studied (the analyte). A titration is carried out for 25.00 ml of 0.100 m hcl (strong acid) with 0.100 m of a strong base naoh (the titration curve is shown in. Titration Base Concentration.
From www.chemicals.co.uk
Titration Experiments In Chemistry The Chemistry Blog Titration Base Concentration \(\text{v}_a\) and \(\text{v}_b\) are the. \(\text{m}_a\) is the molarity of the acid, while \(\text{m}_b\) is the molarity of the base. A titration is carried out for 25.00 ml of 0.100 m hcl (strong acid) with 0.100 m of a strong base naoh (the titration curve is shown in figure. A titration is a laboratory technique used to precisely measure molar. Titration Base Concentration.
From www.reddit.com
How to find concentration from a titration curve? r/chemistryhelp Titration Base Concentration In a titration, a solution of known concentration (the titrant) is added to a solution of the substance being studied (the analyte). \(\text{v}_a\) and \(\text{v}_b\) are the. \(\text{m}_a\) is the molarity of the acid, while \(\text{m}_b\) is the molarity of the base. A titration is carried out for 25.00 ml of 0.100 m hcl (strong acid) with 0.100 m of. Titration Base Concentration.
From www.youtube.com
Worked example Determining solute concentration by acidbase titration Titration Base Concentration A titration is a laboratory technique used to precisely measure molar concentration of an unknown solution using a known solution. In a titration, a solution of known concentration (the titrant) is added to a solution of the substance being studied (the analyte). \(\text{m}_a\) is the molarity of the acid, while \(\text{m}_b\) is the molarity of the base. Titration is performed. Titration Base Concentration.
From www.youtube.com
Finding concentration of acid or base given amount needed to titrate Titration Base Concentration A titration is a laboratory technique used to precisely measure molar concentration of an unknown solution using a known solution. Titration is performed by slowly adding a solution of known concentration to a solution of unknown concentration while observing the reaction. In a titration, a solution of known concentration (the titrant) is added to a solution of the substance being. Titration Base Concentration.